Cloud computing has transformed how organizations build and scale infrastructure. Yet as more workloads move to public clouds, many companies face a harsh reality: cloud costs are increasing faster than expected. According to Forbes, up to 32% of enterprise cloud spend is wasted if proper optimization and governance are not in place (Forbes, 2024).
For enterprises, the challenge is no longer simply cutting costs. The real requirement is optimizing intelligently, keeping performance high while reducing unnecessary spend. Employing the right tools is key to achieving that balance between performance and savings.
Decoding Cloud Cost Optimization
Cloud cost optimization means more than selecting cheaper resources. It is about aligning infrastructure performance with financial efficiency. Each workload consumes resources differently, and what matters is understanding usage behavior, predicting changes, and automating responses that maintain performance without overspend.
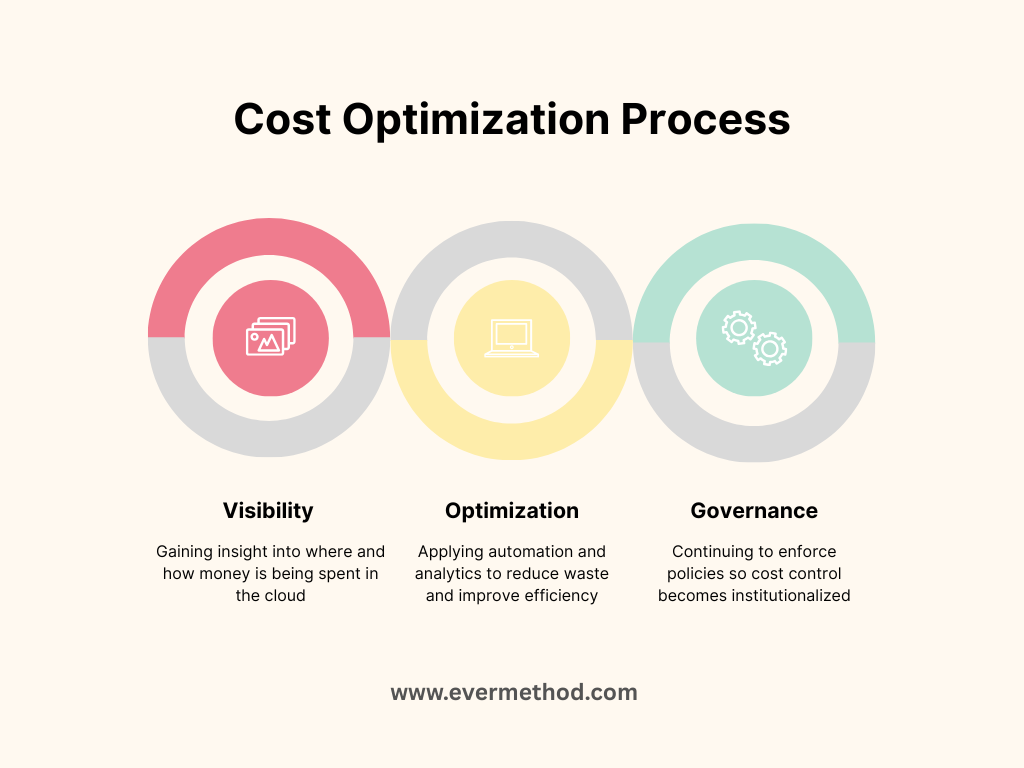
The typical lifecycle of cost optimization involves three major stages:
- Visibility – gaining insight into where and how money is being spent in the cloud.
- Optimization – applying automation and analytics to reduce waste and improve efficiency.
- Governance – continuing to enforce policies so cost control becomes institutionalized.
This approach forms the heart of FinOps, the discipline that connects finance, operations, and engineering so cloud spending becomes a measurable investment rather than an uncontrolled costs.
Key Metrics That Drive Optimization Decisions
Before selecting optimization tools, organizations need a clear set of metrics that link engineering performance to financial outcomes.

The following key metrics outline what to measure, why it matters, and the actions each one should trigger.
1. Utilization Efficiency
- Measures: Compute and memory utilization
- Why It Matters: Detects over-provisioned workloads that unnecessarily inflate cloud spend
- Action Trigger: Apply rightsizing recommendations to align resource capacity with actual demand
- Measures: Unused or detached resources
- Why It Matters: Reveals hidden waste and ongoing costs from idle assets
- Action Trigger: Automate idle shutdowns to eliminate waste and improve efficiency
- Measures: Spend per service, team, or project
- Why It Matters: Improves budget ownership, accountability, and transparency across the organization
- Action Trigger: Enforce consistent tagging policies for precise cost tracking and reporting
- Measures: Throughput or latency relative to cloud spend
- Why It Matters: Balances user experience with financial efficiency, ensuring resources deliver maximum value
- Action Trigger: Reevaluate scaling policies to optimize both performance and cost
- Measures: Ratio of reserved to on-demand usage
- Why It Matters: Maximizes savings through effective use of pricing commitments and long-term reservations
- Action Trigger: Adjust purchasing and commitment strategies to improve cost predictability
Tracking these metrics ensures that cloud cost optimization remains data-driven, repeatable, and aligned with business outcomes not just reactive budget reductions.
Cloud Cost Optimization Tools Overview
Modern cloud environments are complex, often spanning multiple platforms and services. Managing costs manually in such setups is no longer feasible. To maintain both performance and financial control, organizations rely on specialized cost optimization tools that automate visibility, analysis, and resource management.
These tools fall into two broad categories: native tools offered by major cloud providers (AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud) and third-party platforms designed for cross-cloud analytics, automation, and FinOps integration.
Native Cloud Provider Tools
Native tools such as AWS Cost Explorer, Azure Cost Management, and Google Cloud Recommender API provide foundational visibility into cloud spending. They help track resource usage, detect anomalies, and recommend basic cost savings within a single platform.
While effective for initial optimization, they lack the cross-cloud intelligence needed for complex enterprise environments. Each major cloud platform offers its own set of tools that help monitor and optimize spend within its ecosystem.
|
Cloud Platform |
Key Tools |
Primary Capabilities |
Technical Highlights |
|
AWS |
AWS Cost Explorer, AWS Budgets, AWS Compute Optimizer, AWS Trusted Advisor, AWS Cost Anomaly Detection |
Spend analysis, anomaly detection, rightsizing, and automated budget alerts |
Deep integration with AWS CloudWatch and billing APIs |
|
Azure |
Azure Cost Management & Billing, Azure Advisor |
Resource utilization tracking, budgeting, and performance recommendations |
Native Power BI integration and policy automation |
|
Google Cloud |
Google Cloud Cost Management, Recommender API, Committed Use Discounts |
Usage insights, savings recommendations, and sustained discount automation |
Exports billing data to BigQuery for advanced analytics |
These native tools are ideal for initial visibility and quick wins, such as identifying idle resources or over-provisioned instances. However, they are limited to single-cloud environments, which creates a gap for multi-cloud and hybrid strategies.
Third-Party and Multi-Cloud Optimization Tools
Third-party platforms go beyond what native tools provide, offering cross-cloud visibility, automated rightsizing, forecasting, and governance. These tools are designed for enterprises running workloads across multiple cloud providers or Kubernetes clusters.
Third-party platforms like Apptio Cloudability, Spot by NetApp, and Kubecost extend beyond native solutions by offering unified visibility across multiple cloud providers.
They automate rightsizing, forecasting, and governance while applying AI and FinOps principles to drive smarter decision-making. These tools are ideal for enterprises managing hybrid or multi-cloud ecosystems that demand granular analytics and predictive insights.
|
Category |
Tools |
Primary Functions |
Technical Capabilities |
|
Multi-Cloud Cost Management |
Apptio Cloudability, VMware CloudHealth, Flexera One |
Centralizes cost data from AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud |
Advanced policy automation and multi-account governance |
|
AI-Driven Optimization |
Spot by NetApp, Densify, Granulate, Zesty |
Predictive scaling, workload tuning, and real-time resource resizing |
Machine learning models that adjust capacity dynamically |
|
Kubernetes and Container Cost Tools |
Kubecost, CAST AI, Fairwinds Insights |
Pod-level cost visibility and workload efficiency tracking |
Integrates with Prometheus and Helm for container observability |
|
FinOps and Spend Analytics |
CloudZero, Finout, Vantage |
Converts engineering data into business-level cost insights |
Enables unit economics analysis for cloud services |
|
Policy and Governance Automation |
Cloud Custodian, Open Policy Agent |
Enforces tagging rules, shuts down idle resources, and ensures compliance |
Policy-as-code integrated with Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) |
|
Storage and Network Optimization |
Komprise, CloudCheckr, Kentik, Aviatrix CoPilot |
Optimizes data tiering, routing, and egress management |
Reduces hidden network and storage costs |
|
Forecasting and Anomaly Detection |
Anodot, Vantage Forecasts |
Predicts spend trends and detects anomalies using AI |
Supports dynamic alerting and predictive budgets |
These tools enable enterprises to optimize cloud operations holistically, integrating cost data into CI/CD pipelines, security frameworks, and strategic planning. For organizations with hybrid or multi-cloud setups, combining native visibility with third-party intelligence provides the most accurate and actionable optimization strategy.
Best Practices for Implementing Optimization Tools
Adopting tools is only the first step. To realize full benefit, integrate them into your governance and operations.
- Combine native and external tools for layered visibility and intelligence.
- Automate early by shutting down idle resources programmatically.
- Embed cost controls into your deployment pipelines.
- Align optimization outcomes with business KPIs.
- Re-evaluate quarterly as workloads evolve and new savings emerge.
These practices make optimization a continuous process, not a one-off exercise.
Advanced Optimization Approaches
Mature organizations leverage advanced methods such as:
- Predictive autoscaling based on demand modelling.
- Serverless cost profiling for high-precision tuning.
- Dynamic workload migration across regions or providers.
- Unified observability that merges cost and performance dashboards.
These techniques improve not just cost efficiency but also scalability and reliability.
Industry Insight
Forbes reports that executive ownership of cloud cost strategy is essential. When leadership does not oversee cloud efficiency, overspending can erode profitability (Forbes Tech Council, 2025).
Embedding optimization within executive strategy is no longer optional; it is a competitive advantage.
Conclusion
Cloud cost optimization is not a one-time task but an ongoing discipline. By aligning performance and financial efficiency, organizations can turn cloud infrastructure into a driver of profitability. Automation, analytics, and governance together create a smarter, more sustainable cloud ecosystem.
Partner with Evermethod Inc
If your organization is ready to optimize cloud performance, reduce spend, and embed cost efficiency into its operations, Evermethod Inc is your trusted partner.
Our experts specialize in:
- Cloud cost strategy and FinOps implementation
- Cross-cloud tool integration
- Policy-driven automation frameworks
Contact Evermethod Inc today to discover how you can balance performance and savings in your cloud environment.
Get the latest!
Get actionable strategies to empower your business and market domination
.png?width=882&height=158&name=882x158%20(1).png)

.png/preview.png?t=1721195409615)

%2013.png)


